前言 最近在处理ssp-adx-rtb的服务的性能优化,做了好多方面的优化,其中一个就是我们的本地的localcache的问题。
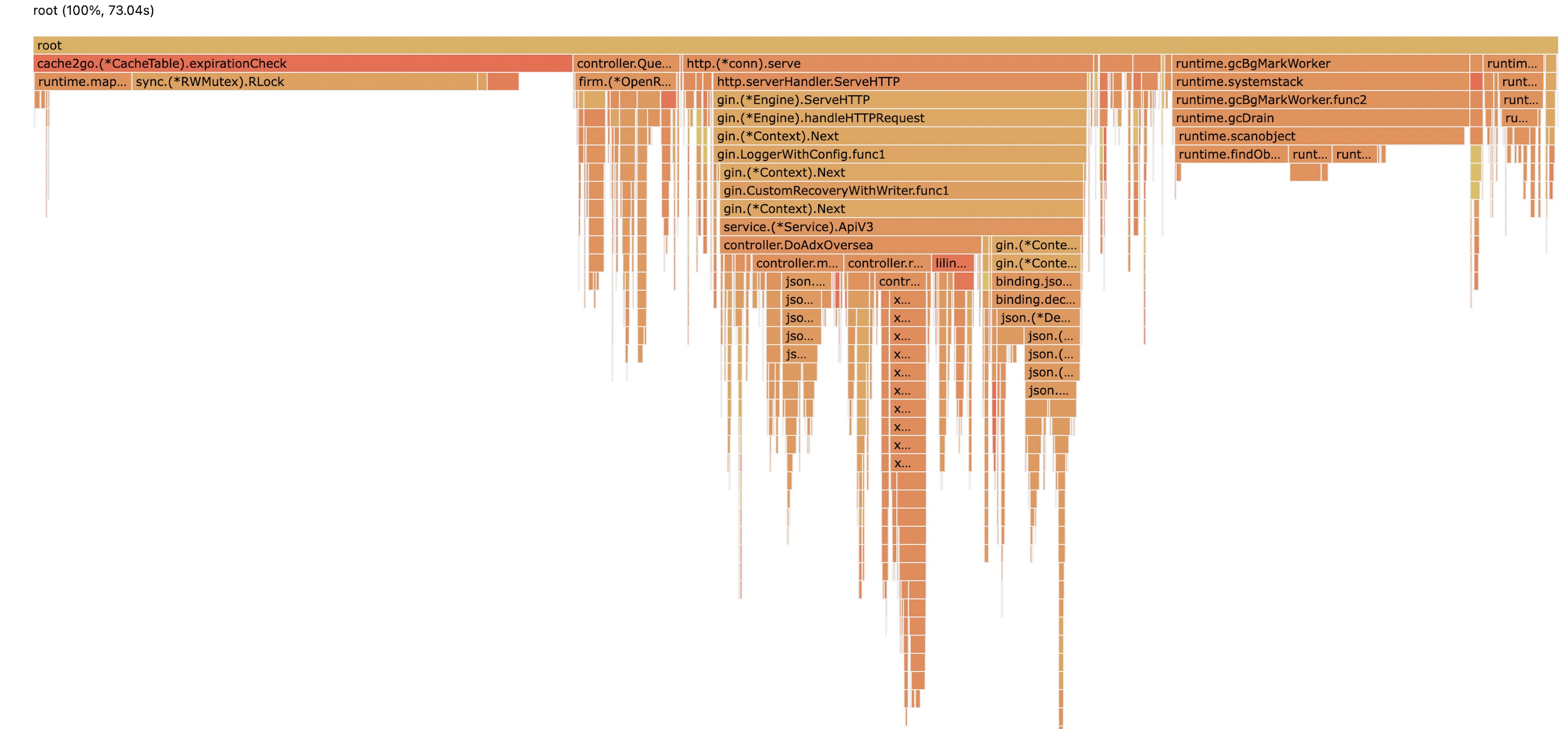
经过pprof的性能分析,发现cache2go,在 CPU Flame Graph 中,占比十分严重,基本大于1/3,既然是localcache,那么,我们的目的本意就是为了提速,所以占比那么大,是十分不合理的。
所以需要找到原因,并且解决它。降低cpu使用率,从而提高服务的QPS,减少服务器成本。
cache2go旧版
项目的描述为:
1 Concurrency-safe Go caching library with expiration capabilities and access counters
并发安全,并且带有效期的和访问计数器的一个类库组件
我们需要用他来解决我们的3大核心问题
对于开源版本第一版本,我们已经做为处理了。
就是他的淘汰策略,是ttl+lru,当一个缓存在一定时间内被连续访问,或者在一个key,准备过期的时候,如果被访问,那么他的过期时间将继续延长到下一个周期。
这一特点,并不是我们需求,所以我们需要对这一点进行了调整,过期时间,只需要判断为 ttl 过期即可,不需要加上 lru 的方式。
这里就不展开细说。
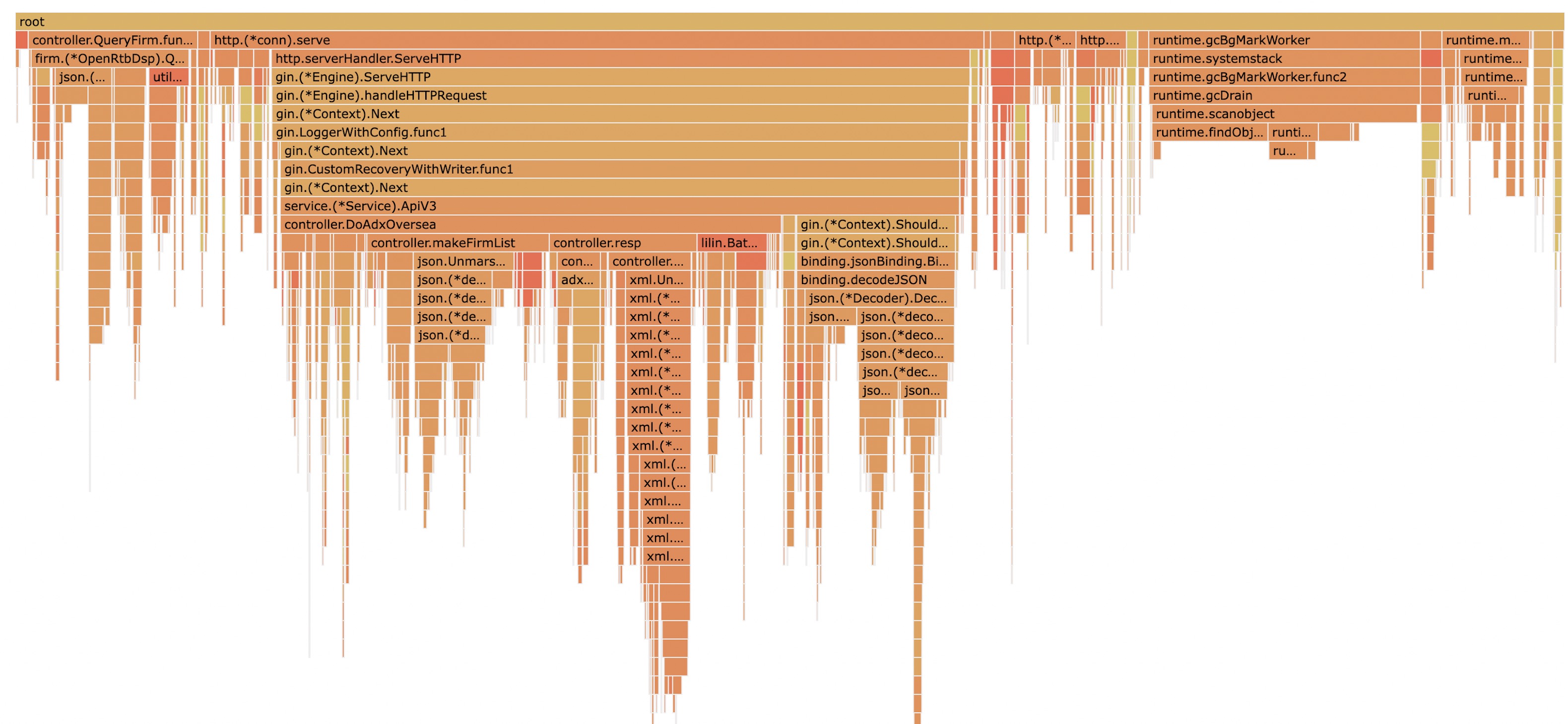
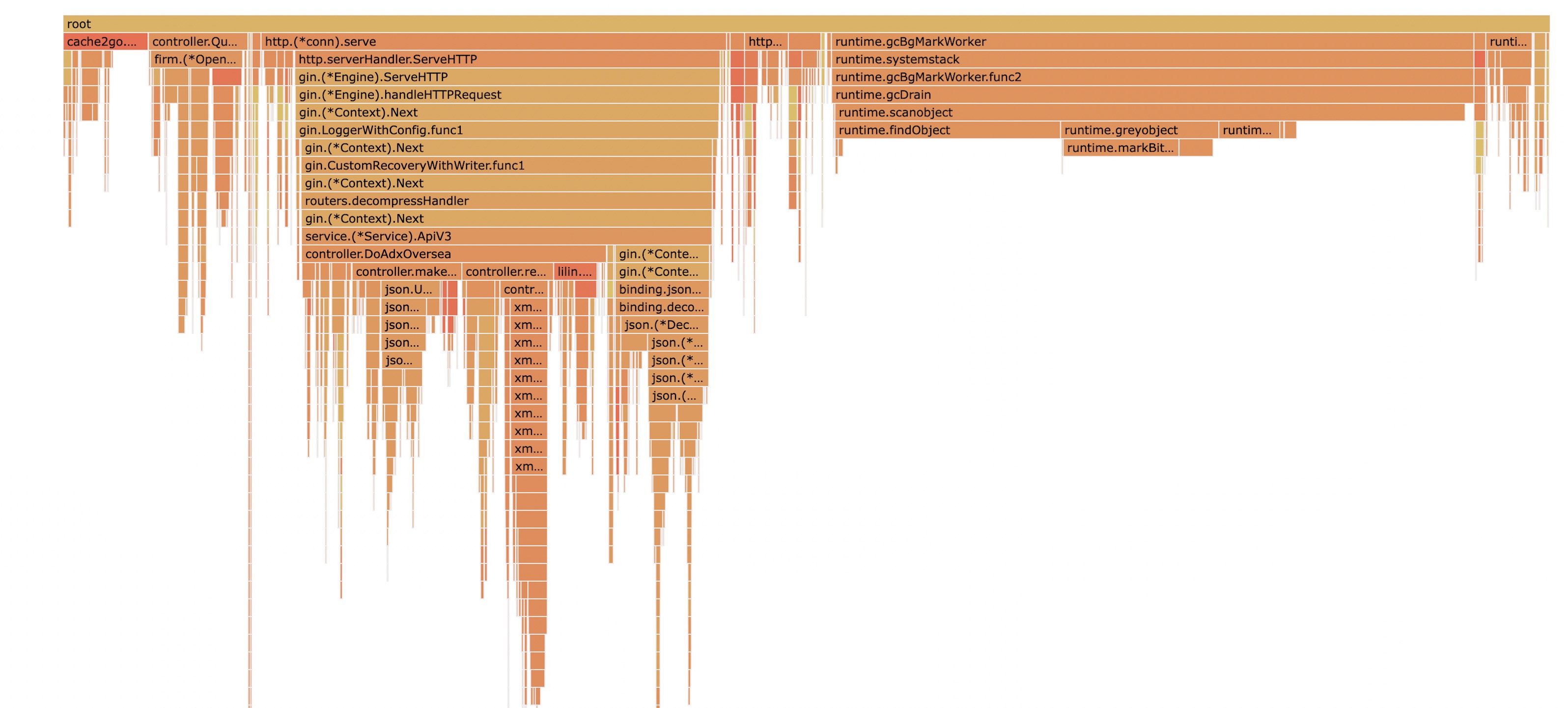
cache2go新版
在这一个版本,基本把整个库都按需重构了。主要是以下几个方面。
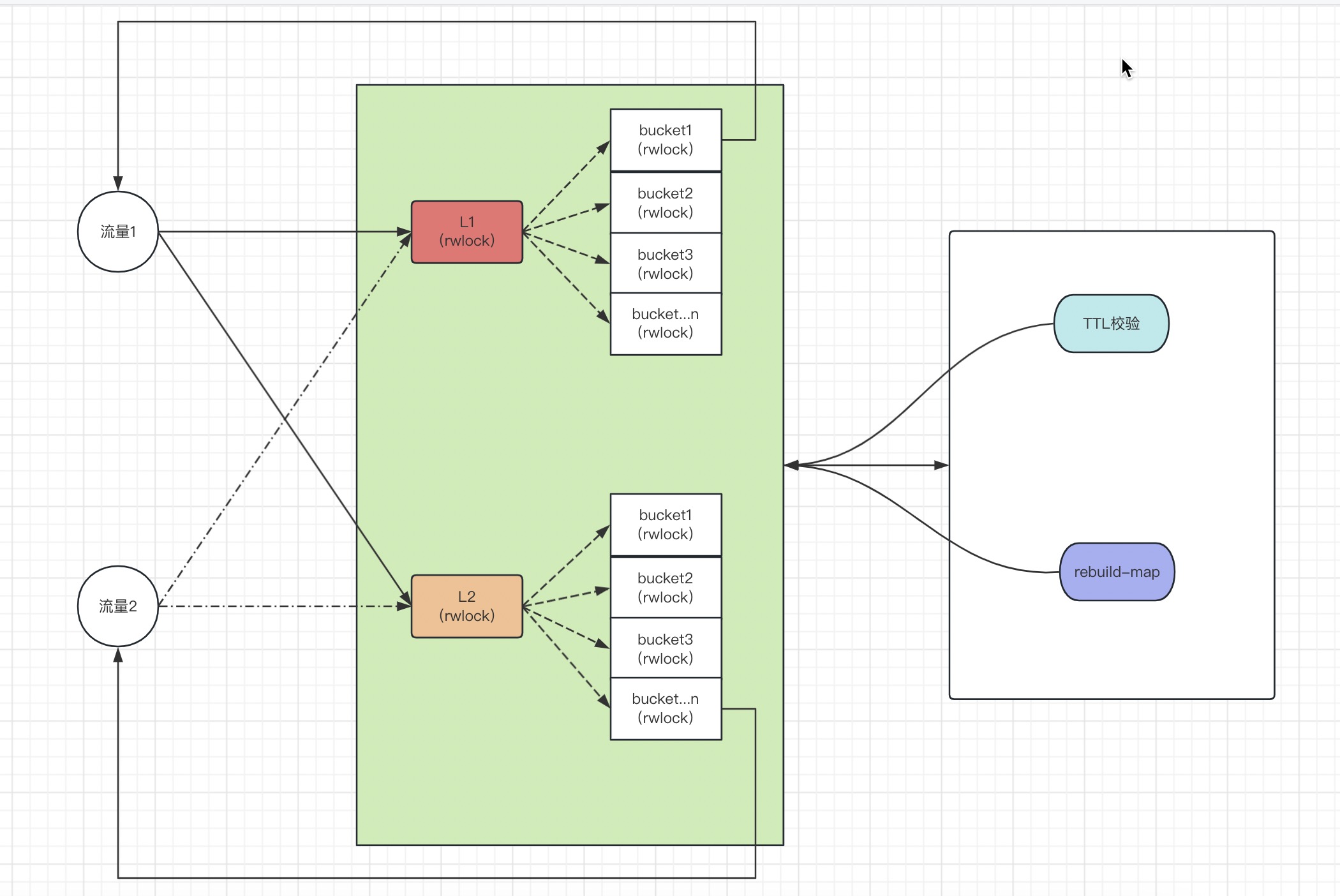
加入hash分片机制,把key打散到不同的bucket中,让bucket-lock的争抢降低
同一个cache-table,有且仅有一个goroutine,来处理 ttl 数据,并不会因为分片的个数调整带来更多的无效goroutine
没有采用渐进式的方式来删除key, 在 add, get 的阶段,尽量保持服务的高效性能,方式由于锁带来的性能衰减
采用双写机制,实现L1和L2的二级包装级别,从而做到 读写分离, 尽可能的避免在必要的场景下由于整个写锁导致读锁阻塞的问题,让后台在处理 ttl 和 重建map的过程中,服务依然高效提供服务
定期重建底层map属性,来释放map申请的内存,让整个服务相对处于一个内存稳定的状态
需求+机制,就可以在读写较多或者后台需要处理map的情况下,性能依旧保持有一个较好的性能体现。
为了实现这几点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 type CacheTable struct { sync.RWMutex hash *fnv64a shardMask uint64 name string L1Shards shardItems L2Shards shardItems cleanupInterval time.Duration l1BlockChan []*CacheItem l2BlockChan []*CacheItem l1Mask int32 l2Mask int32 switchMask uint8 }
Add 这是一个写入过程,实现起来也不算太复杂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 func (table *CacheTable) Add (key interface {}, lifeSpan time.Duration, data interface {}) *CacheItem item := NewCacheItem(key, lifeSpan, data) if table.switchMask != 1 <<1 { atomic.AddInt32(&table.l1Mask, 1 ) defer atomic.AddInt32(&table.l1Mask, -1 ) table.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].lock.Lock() table.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].m[item.key] = item table.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } else { table.l1BlockChan = append (table.l1BlockChan, item) } if table.switchMask != 1 <<2 { atomic.AddInt32(&table.l2Mask, 1 ) defer atomic.AddInt32(&table.l2Mask, -1 ) table.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].lock.Lock() table.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].m[item.key] = item table.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&table.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } else { table.l2BlockChan = append (table.l2BlockChan, item) } return item }
通过双写的方式,实现L1和L2的同时写入,以此达到空间换时间的做法。
其中 (& 2^(n-1)) 做到 (%m)的效果,并且由于是位运算,所以按理说效率会更高
Value
Value 和 就是Get方法,获取key的item
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 func (table *CacheTable) Value (key interface {}, args ...interface {}) (*CacheItem, error) keyBytes, _ := json.Marshal(key) hashedKey := table.hash.Sum64(string (keyBytes)) var sm *shardItem if table.switchMask == 1 >>1 { sm = table.L1Shards[hashedKey&table.shardMask] sm.lock.RLock() r, ok := sm.m[key] sm.lock.RUnlock() if ok { return r, nil } sm = table.L2Shards[hashedKey&table.shardMask] sm.lock.RLock() r, ok = sm.m[key] sm.lock.RUnlock() if ok { return r, nil } return nil , ErrKeyNotFound } else if table.switchMask == 1 <<1 { sm = table.L2Shards[hashedKey&table.shardMask] sm.lock.RLock() r, ok := sm.m[key] sm.lock.RUnlock() if ok { return r, nil } return nil , ErrKeyNotFound } else { sm = table.L1Shards[hashedKey&table.shardMask] sm.lock.RLock() r, ok := sm.m[key] sm.lock.RUnlock() if ok { return r, nil } return nil , ErrKeyNotFound } }
可以看到这里,如果后台没有在操作L1, L2 的话,那么先从L1拿数据,然后再从L2拿数据
如果后台在操作L1, 那么只能从 L2 读取
如果后台在操作L2, 那么只能从 L1 读取
所以通过L1和L2,我们实现了一个读写分离的策略,并且在最大的程度上减少分片锁的读写锁冲突,从而提高服务的效率
后台任务 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 go func (t *CacheTable, ctx context.Context) ticker := time.NewTicker(cleanInterval) reBuildTicker := time.NewTicker(30 * time.Minute) for { select { case <-ctx.Done(): ticker.Stop() reBuildTicker.Stop() return case <-ticker.C: t.Lock() var deleteList []*CacheItem t.switchMask = 1 << 1 now := time.Now() for { if atomic.LoadInt32(&t.l1Mask) == 0 { break } } for i, sad := range t.L1Shards { sad.lock.RLock() for _, r := range sad.m { if now.Sub(r.createdOn).Seconds() > r.lifeSpan.Seconds() { deleteList = append (deleteList, r) } } sad.lock.RUnlock() } for _, item := range deleteList { t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Lock() delete (t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].m, item.key) t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } deleteList = make ([]*CacheItem, 0 ) t.switchMask = 1 << 2 l1Length := len (t.l1BlockChan) for _, item := range t.l1BlockChan { if item != nil { t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Lock() t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].m[item.key] = item t.L1Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } } t.l1BlockChan = make ([]*CacheItem, 0 , l1Length/2 ) for { if atomic.LoadInt32(&t.l2Mask) == 0 { break } } for i, sad := range t.L2Shards { sad.lock.RLock() for _, r := range sad.m { if now.Sub(r.createdOn).Seconds() > r.lifeSpan.Seconds() { deleteList = append (deleteList, r) } } sad.lock.RUnlock() } for _, item := range deleteList { t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Lock() delete (t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].m, item.key) t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } t.switchMask = 1 >> 1 for _, item := range t.l2BlockChan { if item != nil { t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Lock() t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].m[item.key] = item t.L2Shards[item.hashedKey&t.shardMask].lock.Unlock() } } t.l2BlockChan = make ([]*CacheItem, 0 , l2Length/2 ) t.Unlock() case <-reBuildTicker.C: t.Lock() t.switchMask = 1 << 1 now := time.Now() for { if atomic.LoadInt32(&t.l1Mask) == 0 { break } } for _, sad := range t.L1Shards { sad.lock.Lock() nm := make (shard, len (sad.m)) for key, r := range sad.m { if now.Sub(r.createdOn).Seconds() < r.lifeSpan.Seconds() { nm[key] = r } } sad.m = nil sad.m = nm sad.lock.Unlock() } t.switchMask = 1 << 2 for { if atomic.LoadInt32(&t.l2Mask) == 0 { break } } for _, sad := range t.L2Shards { sad.lock.Lock() nm := make (shard, len (sad.m)) for key, r := range sad.m { if now.Sub(r.createdOn).Seconds() < r.lifeSpan.Seconds() { nm[key] = r } } sad.m = nil sad.m = nm sad.lock.Unlock() } t.switchMask = 1 >> 1 runtime.GC() debug.FreeOSMemory() t.Unlock() } } }(t, ctx)